ArachNode
Developing and training an AI model to find information on the web with high metric performance.
Role
Independent
Location
Austin, Texas
Tools
Python, JavaScript, HTML, CSS, Chrome Extensions, TensorFlow, Selenium, AWS, AWS IAM, AWS S3, AWS API Gateway, AWS Lambda, Git
Explore the Project
→ github.com/drebarrera/ArachNode
Challenge
The challenge of ArachNode was to create an AI program capable of navigating the complex and dynamic landscape of the web to identify specific information. Traditional scraping methods often fall short in handling intricate navigation and decision-making. The goal was to design an intelligent system that could provide efficient browsing behavior, making decisions on when to click on links or backtrack, and do so with over 80% accuracy, an Area Under the Curve (AUC) over 0.85, and an F1-score over 0.8.
Solution
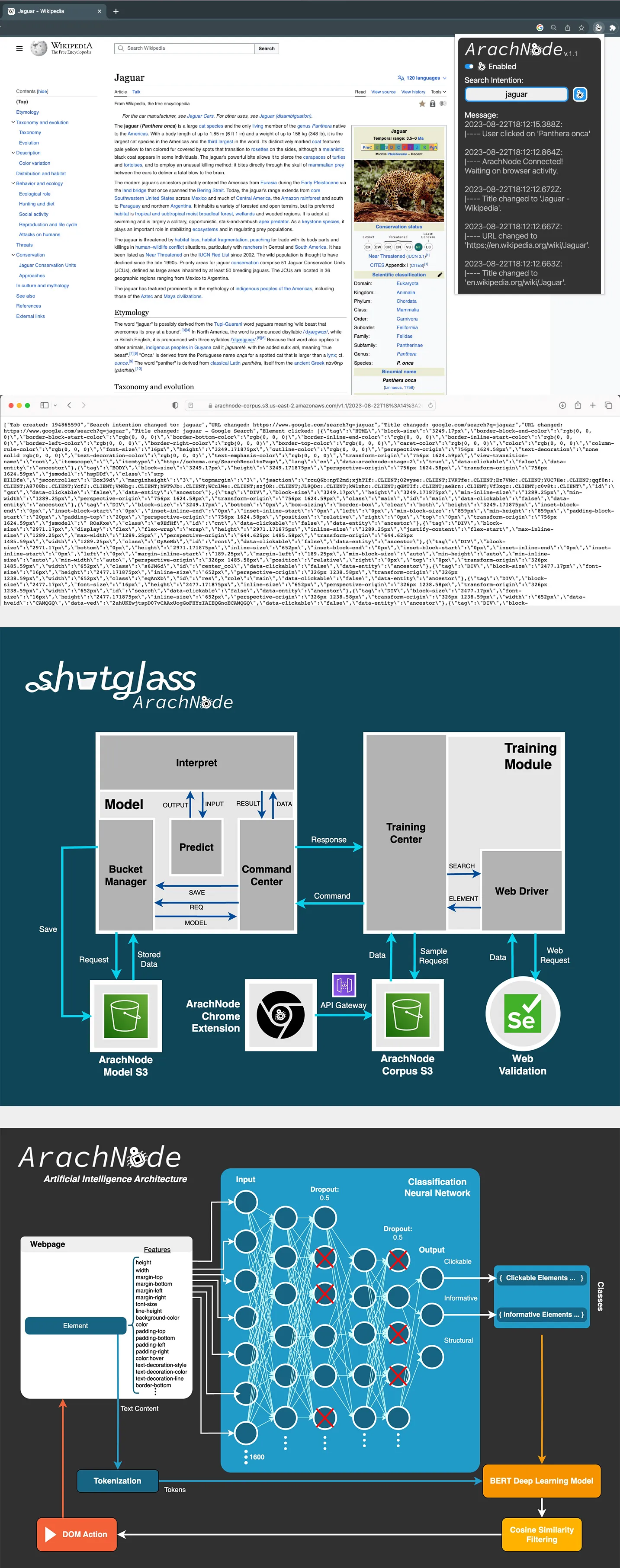
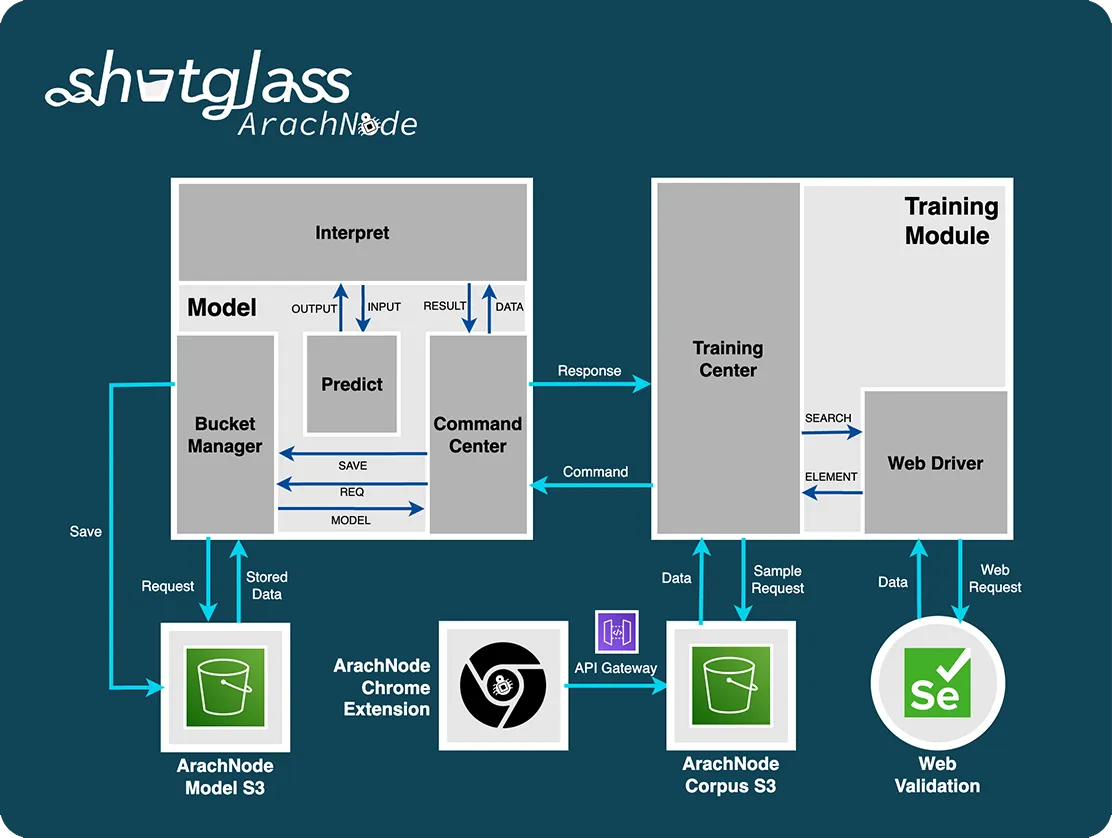
The solution, ArachNode, employs a hybrid approach, integrating feature engineering, machine learning, and advanced NLP techniques like BERT to predict efficient user actions in a web browser. A browser scraper initially collects and quantifies over 1600 DOM-based features, which a trained machine learning model uses to classify web elements into clickable, informative, or structural categories. BERT calculates the 'value of best fit' between each element's text and the user's query, selecting the most relevant action accordingly. The algorithm incorporates a backtracking mechanism, reverting to a previous page if the new document's collective NLP values are suboptimal, thereby ensuring the highest relevance to the user's query.involved designing an AI program using reinforcement learning, a method that allows the system to learn optimal navigation strategies through trial and error.
Development Tools
Design and Development Choices
The ArachNode neural network model, built using TensorFlow's Keras API, is a feed-forward, fully connected architecture with an input layer of 1600 neurons, two hidden layers of 800 and 400 neurons respectively, and an optimized output layer of 3 neurons to match the three categories: clickable, informative, and structural. The model uses ReLU activation functions for computational efficiency and softmax for the output layer. It's configured with an input shape of 1600 to accommodate the extensive feature set derived from DOM attributes. The Adam optimizer and categorical_crossentropy loss function are employed for their suitability in handling large datasets and multi-class classification. To mitigate overfitting, dropout layers have been added. Evaluation metrics include accuracy, AUC, and F1-score to provide a comprehensive assessment of the model's performance. Programmatically, data is collected using a set of Chrome Extension JavaScript functions, stored in AWS S3, and interfaced with using AWS API Gateway. Selenium Python is used for data verification collection.
Result
The ArachNode project is not yet complete, but is underway with training to discriminate between clickable and non-clickable elements (two of the three classifiers given above). Using just 5 search instances with over 1200 DOM elements, the AI has proven to be 32.8% accurate with an AUC of 0.68 and F1-score of 0.45. An AUC higher than 0.5 implies that the model does not apply random guesswork, but the combination of the three metrics leave much room for improvement in precision, recall, and accuracy. The below images show data collection with a custom built Chrome Extension and API, the Python training architecture for the model, and the AI architecture for predicting user browser actions.